Windows 11 hotpatch for clients: security updates without rebooting

Noah Schulz
Consultant Workplace
Modern IT infrastructures require regular security updates that are implemented efficiently and with as little disruption as possible. Especially in productive corporate environments, restarts after Windows updates often lead to a loss of productivity and additional coordination requirements.
With hotpatching, Microsoft provides an innovative update technology that enables selected security updates to be applied without restarting during operation. Until now, this function was primarily reserved for Windows server environments - now it is gradually becoming available for Windows 11 clients as well.
What is hot patching and how does it work?
Traditionally, many Windows security updates require a restart, as security-relevant system components cannot be replaced during operation. This applies in particular to kernel-related services or central system libraries.
Hotpatching fundamentally changes this principle:
Microsoft uses advanced update mechanisms to apply security-relevant changes immediately and seamlessly. The affected programme parts are updated while the system is running - without interruption for users, so that the productivity of your company is maintained.
This is particularly beneficial for central system services, which are often the focus of cyber attacks. Critical security gaps can be closed more quickly, while running applications remain unaffected.
Not every update can be provided as a hot patch, but many critical security updates can be implemented much faster this way.
Availability of hotpatch for Windows 11 clients:
Hotpatch was originally introduced for Windows Server and is now available for clients with Windows 11 version 24H2. It is managed via Windows Update (for private devices) or via corporate solutions such as Windows Update for Business and Microsoft Intune. A suitable edition is required, for example:
- Windows 11 Enterprise E3 or E5
- Microsoft 365 F3
- Windows 11 Education A3 or A5
- Microsoft 365 Business Premium
- Windows 365 Enterprise
Virtualisation-Based Security (VBS) must also be activated. Depending on the configuration, functions such as "Memory Integrity" may be added.
The hot patch update model: baseline updates and hot patches
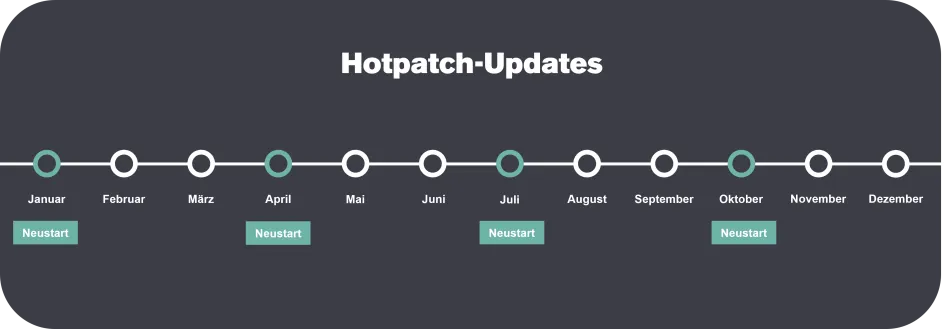
Microsoft combines hotpatching with a clearly defined update cycle:
- Quarterly baseline updates
(January, April, July, October)
→ Reboot required, basic system updates - Monthly hotpatches in the remaining months
→ Security updates without reboot
In exceptional cases, additional hotpatches can also be provided outside of this rhythm, for example in the event of acute security threats.
This model reduces unplanned downtimes and increases the predictability of patch management.
Typical update cycle:
Limits and expectations of hotpatch
Hotpatch significantly improves system availability, but does not replace all reboots. The following updates still require a reboot:
- Feature upgrades
- Driver updates
- Major changes to the operating system
Nevertheless, hot patching can significantly reduce the number of necessary reboots - a clear advantage for the stable operation of modern working environments.
Introduction and best practices for companies:
A structured approach is recommended for the successful introduction of hotpatching:
- Pilot phase:start with 5-10% of representative devices, analysing stability and user feedback.
- Define guidelines:control time windows, deadlines and maintenance times via Windows Update for Business or Microsoft Intune.
- Monitoring and reporting:Use update reports to monitor success rates, exceptions and possible restart requests.
- Consider fallback strategy:unapplied hotpatches are automatically integrated into the next baseline update.
- Transparent communication:Inform your users at an early stage about reduced restarts and fixed update times.
This allows you to sustainably integrate hotpatches into your service, security and compliance processes.
Practice: Monitoring and administration
Hotpatches are clearly recognisable in the Windows update history and are usually marked as not requiring a restart.
For larger environments, Microsoft Intune and Windows Update for Business in particular offer comprehensive options for control, reporting and compliance monitoring. These tools enable centralised management and transparent traceability of all security-relevant updates.
Benefits for IT teams and business operations:
- Significantly reduced system interruptions
- Shorter maintenance windows
- Faster closure of critical security gaps
- Increased end user productivity
- More efficient and flexible patch management
Baseline updates continue to ensure complete system coverage - hotpatch complements this model perfectly.
Conclusion: More security, fewer interruptions
Windows 11 Hotpatch offers companies a modern way of implementing security updates more efficiently. Where technically possible, restarts for monthly security updates are no longer necessary - risks are reduced more quickly while business operations remain stable.
Check the technical and licensing requirements together with your IT team and establish hotpatch as an integral part of your update strategy. Keep an eye on the baseline rhythm and planned feature upgrades.
Claranet supports you in the introduction, integration and optimisation of modern update strategies for Windows clients - in a partnership-based, innovative and solution-oriented manner.
